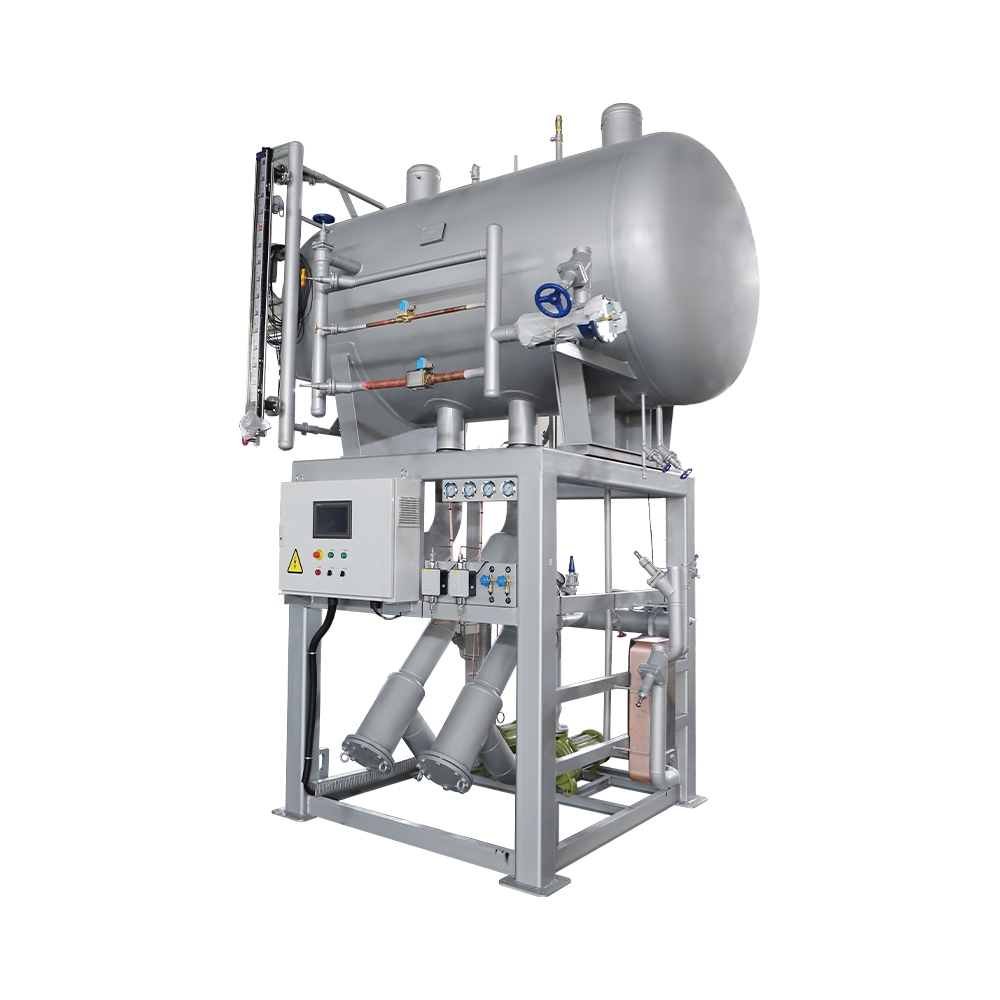
Maximizing Thermal Efficiency with Large-Scale Evaporative Condensing Technology
In the pursuit of operational excellence, modern industrial facilities are increasingly moving away from traditional water-cooled systems in favor of large-scale evaporative condensers. This shift is primarily driven by the equipment's ability to combine the functions of a cooling tower and a water-cooled condenser into a single, highly efficient unit. By utilizing the latent heat of evaporation, these systems can reject heat more effectively than air-cooled alternatives, especially in environments where ambient temperatures fluctuate significantly. For large-scale applications, the ability to maintain lower condensing temperatures translates directly into energy savings of up to 15% to 25% for the entire refrigeration rack.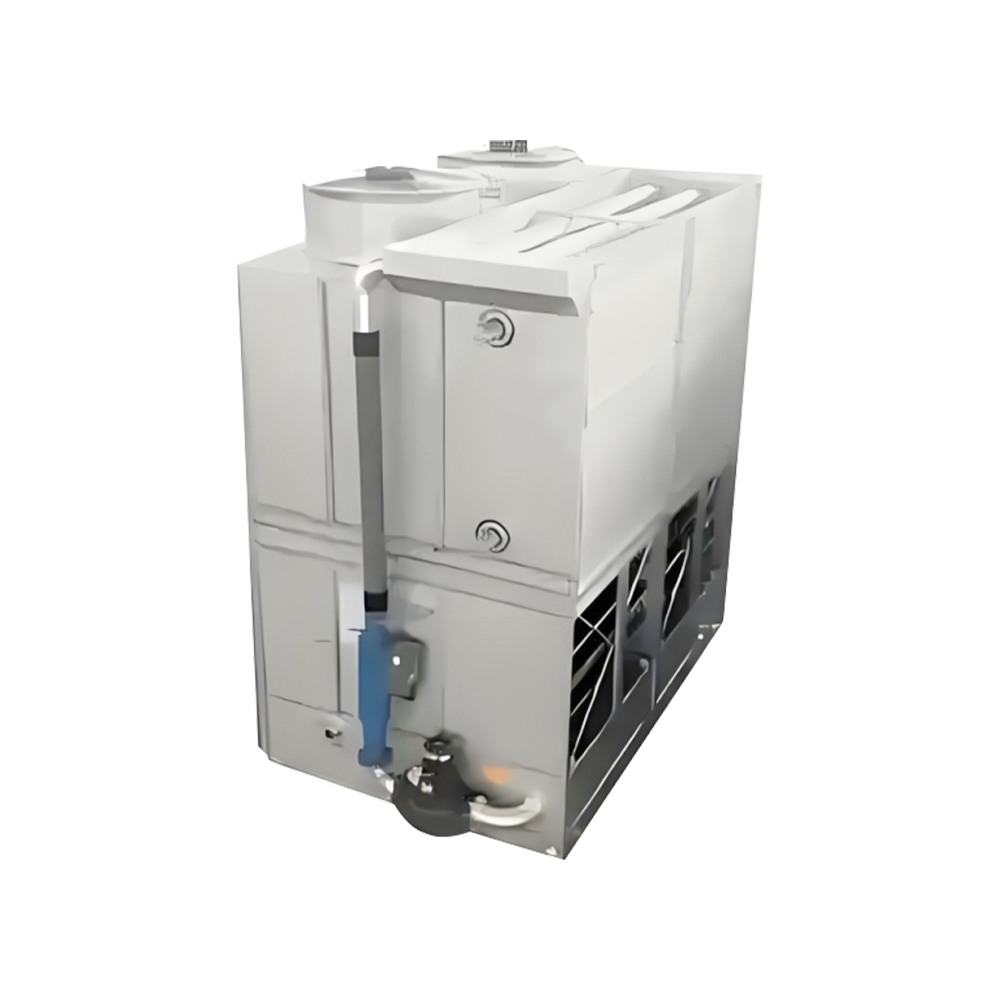
The fundamental advantage of an evaporative condenser lies in its lower condensing temperature, which is tied to the ambient wet-bulb temperature rather than the dry-bulb temperature. This allows the system to operate at a much higher coefficient of performance (COP). When managing large-scale loads, even a 1°C reduction in condensing temperature can result in a measurable decrease in compressor power consumption, making these units the preferred choice for cold storage, chemical processing, and large-scale food manufacturing.
Performance Comparison: Evaporative vs. Traditional Cooling Systems
To understand why large-scale evaporative condensers are a superior investment, it is helpful to look at the resource consumption and operational footprint compared to standard shell-and-tube setups paired with cooling towers. Large-scale units are specifically designed to handle high mass flow rates while minimizing the physical space required on-site.
| System Type | Condensing Temp (°C) | Water Usage (m³/h) | Fan Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air-Cooled | 45 - 50 | 0.0 | 45.0 |
| Water-Cooled + Tower | 35 - 38 | 12.5 | 18.5 |
| Evaporative Condenser | 30 - 33 | 8.2 | 12.0 |
Structural Design and Material Integrity in Large-Scale Units
Given that these units are often installed outdoors and exposed to the elements, material selection is a critical factor for long-term reliability. Large-scale evaporative condensers typically utilize heavy-duty hot-dip galvanized steel or stainless steel for the casing and coil sections. This construction protects the unit against the corrosive nature of constant water evaporation and mineral buildup.
The Importance of Advanced Coil Technology
The heart of the condenser is the condensing coil. In large-scale systems, the coil design must balance internal refrigerant pressure drop with external air and water flow. Elliptical or sloped tube designs are often employed to ensure that the condensed liquid refrigerant drains quickly to the receiver, preventing "liquid backing" which can drastically reduce the effective heat transfer area. High-performance units are tested at pressures exceeding 2.5 MPa to ensure safety and compliance with global pressure vessel standards.
Optimized Airflow and Drift Elimination
To protect the surrounding environment and save water, modern evaporative condensers incorporate high-efficiency drift eliminators. These components capture water droplets entrained in the discharge air stream, reducing water loss to less than 0.001% of the recirculating water rate. This not only conserves resources but also prevents the spread of mineral deposits on nearby equipment.
Key Maintenance Strategies for Industrial-Scale Condensers
Because large-scale evaporative condensers process vast quantities of air and water, they are susceptible to scaling and biological fouling. Without a proactive maintenance plan, the heat transfer efficiency can degrade rapidly, leading to high head pressures and potential system shutdowns.
Industry-standard maintenance practices include:
- Automated Water Treatment: Implementing "blowdown" cycles to maintain the Cycles of Concentration (CoC) at a level that prevents scale formation while minimizing water waste.
- Nozzle Inspection: Checking the spray distribution system monthly to ensure the entire coil surface is wetted, preventing "dry spots" that lead to rapid scaling.
- Fan Drive Maintenance: Large-scale units often use belt-drive or direct-drive axial fans; ensuring proper tension or lubrication prevents mechanical failure during peak summer loads.
- Sump Cleaning: Removing accumulated silt and debris from the cold water basin to prevent pump clogging and nutrient sources for bacteria.
Future-Proofing Your Facility with Hybrid Evaporative Solutions
As water scarcity becomes a more pressing global issue, many large-scale evaporative condensers are now being equipped with variable speed drives (VFDs) and hybrid controls. These systems can operate in "dry mode" during colder months, completely eliminating water consumption when the ambient air is sufficient to handle the heat load. Transitioning to a smart, large-scale evaporative system is not just about current performance; it is a strategic move to ensure compliance with evolving environmental regulations and rising utility costs.
By investing in high-quality evaporative technology, facilities secure a reliable cooling foundation that balances high-capacity heat rejection with the lowest possible energy footprint.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体






